Content
- What is TELA
- Signs and symptoms
- The clinical picture of PE on ECG
- An example of a clinical picture on an ECG
- Additional diagnostic methods
- Patient hospitalization
- How is PE treated
- Surgical procedures
- Thrombolytic therapy
- Initial anticoagulant therapy
- Supportive anticoagulant therapy
- Systemic thrombolytic therapy
- Diet for PE
- Forecasts
- Video about ECG with pulmonary embolism
PE on the ECG is manifested by the presence negative T wave at once in 2 leads VI and V3. Similar results of a hardware study of the cardiovascular system indicate an embolism of one or two pulmonary arteries at once. Patients with this electrocardiogram of the heart have pathological signs in the form of shortness of breath, palpitations, dizziness, blue skin in the lips.
What is TELA
PE is a thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries, which is considered a complication of venous thrombosis. The occurrence of this pathology is caused by the sudden separation of a blood clot. A dense clot of platelets migrates through the general bloodstream from the site of its primary localization to the pulmonary arteries. This leads to an acute disturbance of blood circulation in large arterial vessels.
In most cases, PE is the cause of death. The main danger of this disease is that its symptoms can be disguised as other cardiac diseases. Timely ECG allows diagnosing pulmonary embolism in the early stages of its development.
In 90% of cases, the main source of blood clots that block blood circulation in the pulmonary arteries are the deep veins of the legs. Most patients with signs of PE are diagnosed with thrombosis of the inferior vena cava, renal and pelvic veins.
Floating blood clots are recognized as embolic. These are platelets that are only partially attached to the wall of the venous vessel. Physical activity, a sharp change in body position, unstable blood pressure can provoke a sudden separation, as well as further migration of this thrombus. Flotation of the cardiovascular system is found in 26% of patients admitted to the hospital of the cardiology department with a diagnosis of PE.
Signs and symptoms
PE on an ECG (signs of this pathology are determined by a cardiologist or therapist) is detected by a doctor in the process of decoding the results of this diagnosis.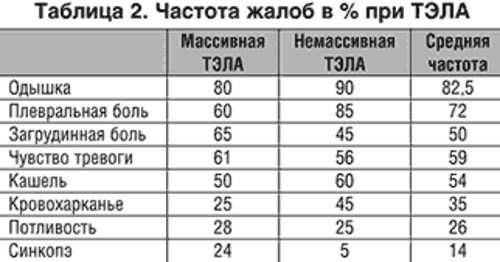
In patients with pulmonary embolism, the following symptoms are present:
- feeling short of breath;
- pain in the chest area;
- heart palpitations (heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute);
- cyanosis of the skin, which is most noticeable in the area of the lips, fingers of the lower extremities;
- thrombosis of the venous vessels of the legs;
- dry, incessant cough, which intensifies at the time of the next attack of tachycardia;
- sharp pain inside the chest;
- coughing up blood clots;
- a state of fever;
- a sharp increase in body temperature to a level of 38.5 degrees Celsius;
- tachypnea.
Most patients with PE have the above symptoms. The ECG results only confirm the fact of the pathological condition of the pulmonary arteries. Patients with these signs of deterioration in health require emergency hospitalization.
The clinical picture of PE on ECG
Thromboembolism of the pulmonary arteries is manifested by signs of significant overload, or damage to the tissues of the right parts of the heart muscle. During the ECG, the patient has a characteristic SIQIII syndrome. In this case, the deep S-waves in the standard lead, as well as the Q-waves, are combined with the T-waves in lead III.
A patient with signs of PE is necessarily found to have a blockade of the anterior branch of the bundle branch on the left. T-type negative waves are present in the chest leads of the V1-V4 segment. The pointed P wave, which is located in lead II, is too high (within 12.5 mm).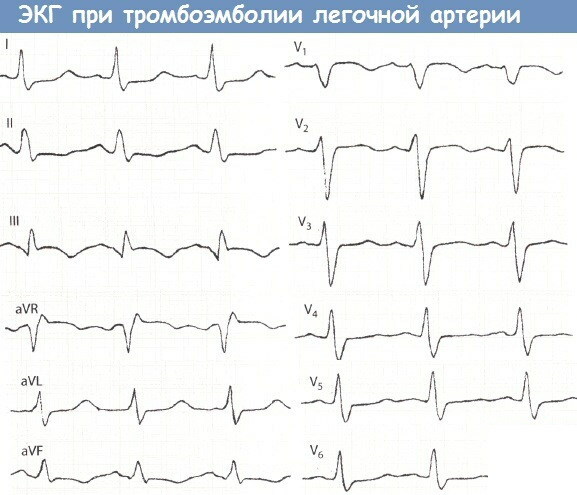
These manifestations of the clinical picture of PE are considered nonspecific, since they can be diagnosed in patients with other cardiopulmonary diseases of the chronic and acute forms of the course.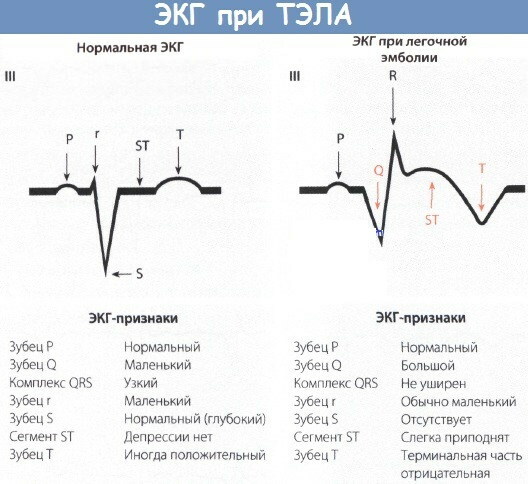
In cardiological practice, there are occasional cases when, even in conditions of massive and submassive PE, the ECG results remain relatively normal. On average, 33% of patients admitted with signs of thromboembolism have SIQIII syndrome using an electrocardiogram.
An example of a clinical picture on an ECG
Below is an example of the clinical picture of PE on an ECG in a 68-year-old patient who has concomitant diseases of the body in the form of an exacerbation of the chronic form of thrombophlebitis, coronary insufficiency, cardiosclerosis:
- there is a syndrome of the SIQIII type, and the QRS is equal to 0.08 s;
- the RS-TIII segment is displaced upward;
- segment RS-TI and V6 are directed down;
- wide TIII wave merges with negative U wave;
- the QII wave is abnormally small in size;
- the tooth of the QaVF type is too pronounced, but its width does not exceed 0.03 s.
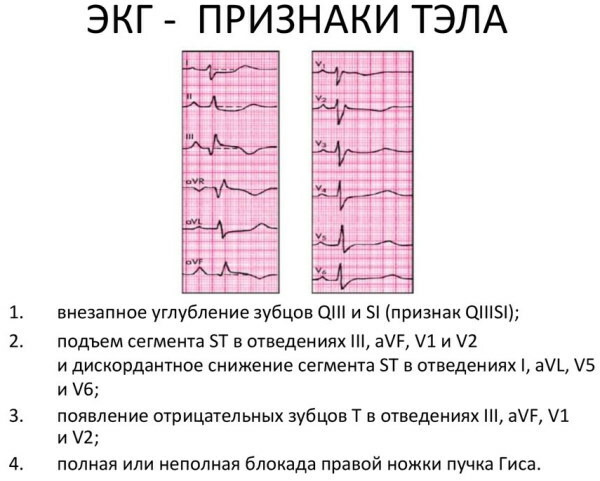 As PE progresses, the functions of the patient's cardiovascular system deteriorate. The patient's pathological condition is displayed by the corresponding ECG results.
As PE progresses, the functions of the patient's cardiovascular system deteriorate. The patient's pathological condition is displayed by the corresponding ECG results.
Additional diagnostic methods
In combination with ECG, other methods of detecting signs of PE are used. The table below describes the following additional methods for diagnosing this pathology.
| Inspection method | Diagnostic characteristics |
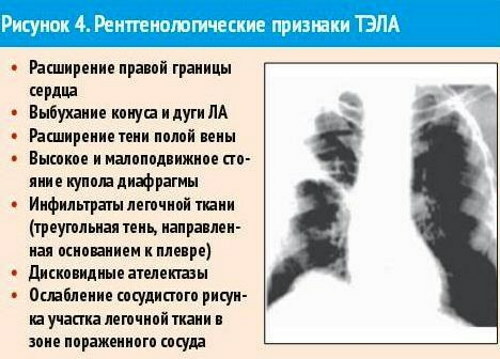
| X-ray | X-ray examination of the chest organs confirms or refutes the presence of pulmonary hypertension, the presence of which is characteristic of patients with pulmonary embolism. In most cases, the radiograph reveals infiltrative foci in the area of tissue damage, as well as the following signs of PE:
The appearance of the latter sign is observed directly in the area of thromboembolic lesions of an arterial vessel. Repeated chest x-ray examination 5-7 days from onset the first signs of PE shows that the damaged lung tissue of the patient has symptoms of infarction pneumonia fabrics. A similar clinical picture is diagnosed in 36% of patients with thromboembolism. |
| Echocardiography | Echocardiography is a modern and informative method for determining PE using ultrasound. Using this diagnostic method, the following signs of thromboembolism are detected:
The use of the echocardiography method allows for differential diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and other cardiac pathologies, the development of which has similar symptoms, but is accompanied by additional myocardial damage. |
| Analysis of venous blood for the level of cerebral natriuretic peptide and D-dimer | The biological substance D-dimer is a product of the breakdown of fibrinogen. The concentration of this component in the blood plasma varies depending on the degree of activity of the processes associated with thrombus formation. A normal D-dimer reading indicates no thromboembolism. The level of this substance over 500 μg per 1 liter of venous blood is a clinical sign of an acute form of thrombosis of the great vessels, as well as one of the obvious symptoms of PE. Brain natriuretic peptide concentration is a biological marker for stratification of the potential risk of PE. An indicator of this substance over 90 pg per 1 ml of blood indicates the presence of thromboembolism with the risk of death. |
 Depending on the general condition of the patient, the results of the examination, the presence of concomitant diseases of the body, the attending physician may prescribe the patient to undergo other diagnostic methods.
Depending on the general condition of the patient, the results of the examination, the presence of concomitant diseases of the body, the attending physician may prescribe the patient to undergo other diagnostic methods.
Patient hospitalization
PE on the ECG (signs of arterial thrombosis appear suddenly) is displayed by changes in the sharpness of type S waves. Patients with symptoms of acute thromboembolism require immediate hospitalization in the cardiology department.
Patients with signs of pulmonary embolism receive the following emergency care:
- saturation of blood flow with an additional volume of oxygen, if the saturation level is below 95%;
- intravenous infusion of Dobutamine solution at a dosage of 5 to 20 μg per 1 kg of body weight;
- drip injection of the drug Norepinephrine in an amount of 2 to 30 mcg per minute. (the use of this medication is indicated for patients with low blood pressure);
- single injection of UFH at a dose of 80 IU per 1 kg of patient weight.
With the help of these therapeutic measures, the effect of preliminary stabilization of the general condition of the patient with PE is achieved, and the risk of sudden death is minimized. After that, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination of the cardiovascular system. Based on the results of the diagnosis, the attending physician selects other drugs for the patient to prevent thromboembolism.
How is PE treated
PE on an ECG (signs of a painful condition of the pulmonary arteries are determined during the preliminary examination of the patient) is manifested by the SIQIII syndrome. The tactics of treating thromboembolism depends on the severity of this pathology and the degree of risk of death.
Surgical procedures
Patients who are contraindicated in the use of systemic thrombolytic therapy are prescribed embolectomy surgery. This type of treatment involves open surgery to remove a blood clot from the pulmonary artery cavity.
The result of the surgical operation is the unblocking of the main vessel with the restoration of normal blood flow. Patients with a risk group for recurrent pulmonary embolism undergo installation of a venous filter, which prevents the re-entry of a blood clot from the veins of the lower extremities.
Thrombolytic therapy
Thrombolytic therapy involves the use of a recombinant plasminogen activator. This substance is prescribed at a dosage of 100 mg every 2 hours. Intravenous administration of a recombinant plasminogen activator in the form of a drop solution is carried out in doses of 0.6 mg per 1 kg of the patient's body weight. The jet supply of the drug is performed within 15 minutes.
It is important to remember that thrombolytic therapy has the following contraindications for its use:
- previous hemorrhagic stroke of the brain;
- during the last month the patient has suffered severe tissue trauma or extensive surgery;
- there is a reasonable risk of gastric bleeding opening;
- within the last 6 months. the patient suffered an ischemic cerebral stroke
- an extraneous neoplasm of an oncological or benign nature was found in the structure of the patient's central nervous system.
Thrombolytic therapy is also not recommended for patients who have recently undergone traumatic resuscitation, puncture, take oral anticoagulants, or are in a state pregnancy.
Initial anticoagulant therapy
At the initial stages of treatment of PE, all patients with this diagnosis are shown the use of anticoagulant therapy. Taking drugs of this category provides blood thinning, and also prevents the formation of blood clots.
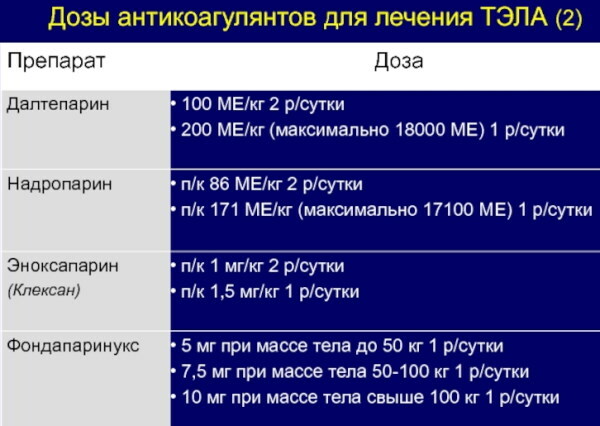
The table below shows a list of anticoagulant medications that are used at the initial stage of therapy:
| Name of the medicinal product | Standard dosage regimen | The frequency of use of the medication |
| Unfractionated form of heparin | Not more than 10,000 IU | The frequency of drug administration depends on the parameters of the biochemical composition of the patient's blood. |
| Nadroparin | From 86 to 171 IU per 1 kg of the patient's body weight | The medication is applied once a day, or it is administered every 12 hours. |
| Fondaparinux | Patients weighing less than 50 kg receive a dose of 5 mg. If you have a weight of 50 to 100 kg, the dosage regimen is 7.5 mg. Patients weighing over 100 kg receive a standard dosage of 10 mg. | The drug is prescribed for use no more than 1 time per day. |
| Enoxaparin | From 1 to 1.5 mg per 1 kg of the patient's body weight. | The drug is taken once a day. |
| Warfarin | The dosage regimen is determined by the attending physician individually. This medication is prescribed in combination with Fondaparinux. | This anticoagulant is taken once a day. |
Throughout the entire period of anticoagulant therapy, the patient is in the hospital of the cardiology department under the supervision of medical personnel. Particular attention is paid to the results of the analysis of venous blood for platelet levels.
Supportive anticoagulant therapy
To prevent recurrent PE, improve blood circulation in the venous and arterial vessels, a patient who has previously suffered thromboembolism receives maintenance anticoagulant therapy with the following drugs:
- Warfarin;
- Apixaban;
- Rivaroxaban;
- Low molecular weight heparin (administered subcutaneously to patients who are at a special risk group for recurrent PE);
- Aspirin for blood thinning.
The dosage regimen with the above medicines is determined by the doctor depending on the state of the patient's cardiovascular system, his age, the risk of recurrent thromboembolism. The minimum duration of maintenance anticoagulant therapy is 3 months. In severe cases, taking these drugs can be lifelong.
Systemic thrombolytic therapy
The use of systemic thrombolytic therapy is indicated in patients at high risk of recurrent thromboembolism. The principle of action of thrombolytic drugs is to dissolve blood clots, which are localized inside the blood vessels. Systemic therapy with these medications provides timely prevention of acute impairment of blood flow in the pulmonary arteries.
In this case, drugs of the following types can be used:
- Alteplase;
- Retaplase;
- Urokinase;
- Tenekteplaza.
The systemic thrombolytic therapy regimen is drawn up by the attending hematologist or cardiologist. The dosage regimen with the above medicines and the timing of treatment are determined for each patient individually.
Diet for PE
The diet for patients with thromboembolism contains high levels of potassium, magnesium and calcium. These minerals are essential for maintaining stable heart and blood vessel function. This diet minimizes the amount of animal fats and carbohydrates that contribute to overweight.
Patients with pulmonary embolism are allowed to consume the following foods and drinks:
- wheat flour bread (only yesterday's or well-dried);
- biscuit;
- seafood;
- beef;
- biscuits without added trans fats and baker's yeast;
- edged pork;
- vegetable soup (average weight of 1 portion is from 250 to 400 g);
- boiled potatoes;
- rabbit meat;
- chicken;
- low-fat milk;
- kefir;
- cottage cheese with a minimum fat content;
- soft-boiled chicken eggs (no more than 1 pc.);
- all types of legumes;
- cottage cheese, rice or vegetable casserole;
- pasta;
- cereals;
- vegetables baked in the oven, boiled in water or in a steam bath;
- compote;
- weak tea with the addition of a lemon wedge;
- a decoction of rosehip berries;
- lean river fish.
For patients with thromboembolism, the following foods and drinks are strictly prohibited:
- coffee;
- spicy and fatty sauces;
- ketchup;
- chocolate;
- celery;
- fatty meats;
- fresh bakery;
- fried pancakes and pancakes;
- soups with mushroom, fatty meat or fish broth;
- onion;
- all types of smoked meats;
- mutton;
- alcohol;
- fried eggs;
- garlic;
- canned meat and fish;
- celery;
- sweet soda;
- basil;
- radish;
- salty fish.
Diet table number 10 is observed by patients with pulmonary embolism throughout the entire course of drug therapy. Eating foods low in animal fats prevents recurrence of thromboembolism in patients who have previously encountered this pathology.
Forecasts
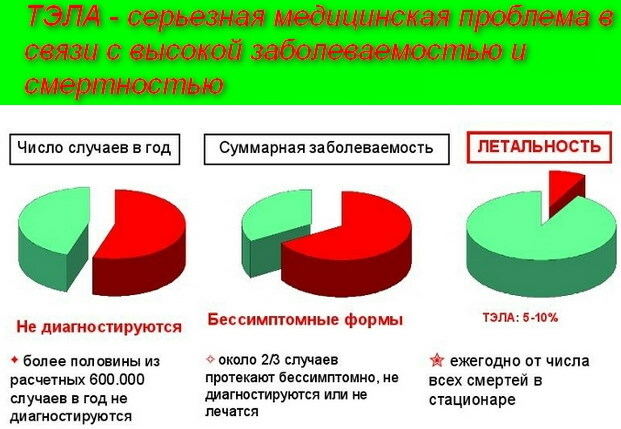
On average, 10% of patients with PE die in the first 1-3 hours after the first signs of this disease appear. In most people, thromboembolism causes sudden cardiac arrest and death. If a blood clot enters the pulmonary artery cavity, the prognosis for complete recovery is unfavorable.
To reduce the risk of death from PE, the following guidelines are recommended:
- regularly undergo a preventive examination of the heart and blood vessels (every 6 months);
- immediately contact a cardiologist or therapist in case of the appearance of primary signs of thromboembolism;
- in the presence of symptoms of venous thrombosis, take anticoagulant drugs.
 The prognosis for PE is especially unfavorable for patients who have a tendency to increased thrombus formation, and have previously been admitted to the hospital of the cardiology department with signs thromboembolism.
The prognosis for PE is especially unfavorable for patients who have a tendency to increased thrombus formation, and have previously been admitted to the hospital of the cardiology department with signs thromboembolism.
PE is a pathology of the pulmonary arteries that develops as a result of thrombosis of the venous vessels of the legs. The clinical sign of this disease is shortness of breath, tachycardia, dry cough, dizziness.
The main cause of thromboembolism is the separation of a thrombus from the vein wall with its further entry into the pulmonary artery cavity. Acute disturbance of blood flow in the great vessels leads to the collapse of the heart muscle and respiratory system. ECG is one of the diagnostic methods for pulmonary embolism.
Video about ECG with pulmonary embolism
ECG for PE:
