Content
- Requirements for blood components for transfusion
- Mechanism of action of transfused blood
- Substitution action
- Hemodynamic
- Detoxification
- Hematopoietic
- Immunological
- Hemostatic
- Nutritional
- Stimulating
- Main indications for blood transfusion
- Indications for the use of blood transfusion drugs
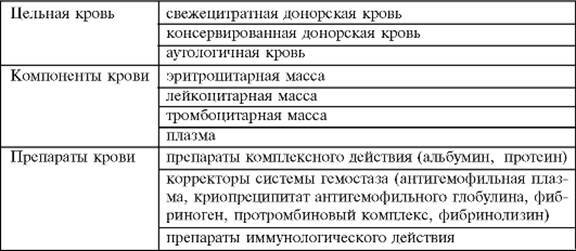
- Whole blood
- Cellular components of blood
- Plasma preparations
- Indications for different types of blood transfusion
- Red blood cell transfusion
- Plasma transfusion
- Platelet transfusion
- Cryoprecipitate transfusion
- Leukocyte transfusion
- Who can blood transfusions be from?
- Contraindications to blood transfusion
- Complications of blood component transfusion
- Blood transfusion videos
Blood transfusion from donor to recipient Is a complex medical procedure that is indicated for prescription to stabilize vital functions in patients with an acute form of blood loss, intoxication of the body, septic and hemorrhagic shock.
Requirements for blood components for transfusion
The table below shows the legal requirements for the quality of donated blood that must be transfused to a recipient.
| Components of biological material | Indicator of the norm |
| Overall volume | 450 ml |
| Hemolysis of erythrocytes | Not more than 0.8% of the total mass of red blood cells |
| Hematocrit | 0.65 to 0.75 |
| Hemoglobin | Not less than 45 units in 1 dose |
| Leukocytes | No more than 1.2 x 10 in the 9th power |
| Osmolarity | Not less than 340 milliosmoles per 1 liter of blood |
| Sterility | Absolute sterility |
| Platelets | Not less than 60 x 10 in the 9th degree |
| NS | 6.4 to 7.4 units |
| Erythrocytes | Not more than 6 x 10 in the 9th degree per 1 liter of venous blood |
| Factor VIIIC | Not less than 70 units |
| Fibrinogen | Not less than 140 mg |
| Granulocytes (volume) | No more than 500 ml |
| Quantitative indicator of granulocytes | More than 10 x 10 to the 9th power |
Whole blood and its components in the form of erythrocytes, which will be immediately used for transfusion, are stored for a short period of time at a temperature of +2 to +6 degrees Celsius. Fresh frozen plasma, as well as cryoprecipitate, should be kept within the temperature range of -25 degrees Celsius. Shelf life up to 36 months.
Mechanism of action of transfused blood
Donated blood has a direct effect on all physiological processes in the recipient's body.
Substitution action
Blood transfusion is indicated for patients who have suffered acute blood loss. For this, whole donor blood is used. The erythrocytes introduced into the patient's body restore the required volume of biological fluid, and also provide a stable course of gas exchange processes.
Donated blood leukocytes increase the resistance of the immune system in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms. Platelets regulate the rate of blood clotting. Albumin and plasma activate hemodynamic processes. Lipids, proteins and fats that enter the recipient's body along with donor blood are included in a series of biochemical reactions.
Hemodynamic
It has been scientifically proven that blood transfusion from a donor to a recipient has the following hemodynamic effect on the latter's body:
- expansion of venules and arterioles;
- acceleration of blood flow;
- opening the network of the smallest vessels of the capillaries;
- reduction of the lumen of arteriovenous shunts.
After 1-2 days after the completion of the blood transfusion, the recipient has an increased flow of lymph from the soft tissues into the general bloodstream. As the patient recovers, further stabilization of hemodynamic processes occurs.
Detoxification
Indications for blood transfusion is a list of clinical cases in which the performance of blood transfusion is a vital action. Donated blood is used to replace the recipient's own blood if there are signs of its oversaturation with toxins.
Blood transfusion accelerates the process of natural detoxification of the patient's body, and also prevents the development of irreversible changes in the work of the kidneys, heart, liver, central and peripheral nervous systems. Timely injected donor blood normalizes the water-electrolyte balance, which was disturbed as a result of poisoning with toxins.
Hematopoietic
The hematopoietic effect of donor blood is that its components activate the work of the bone marrow and other hematopoietic organs of the recipient. The erythrocyte mass supplied during transfusion normalizes the physiological process for the synthesis of new cellular blood components.
Immunological
Granulocytes, immunoglobulins, macrophages and lymphocytes, which are contained in donor blood, increase the recipient's immunity. In the patient's body, the physiological mechanism of the formation of its own antibodies is triggered in relation to bacterial, viral, fungal infections. The phagocytic functions of leukocytes increase. Blood obtained from initially immunized donors has a special immunological effect.
In the patient's body, the physiological mechanism of the formation of its own antibodies is triggered in relation to bacterial, viral, fungal infections. The phagocytic functions of leukocytes increase. Blood obtained from initially immunized donors has a special immunological effect.
Hemostatic
Indications for blood transfusion include mandatory blood transfusion for patients who have suffered internal bleeding. The hemostatic effect of donated blood is to stimulate the recipient's hemostasis. The patient has moderate hypercoagulation, which occurs due to an increase in the thromboplastic activity of the blood.
Blood preparations in the form of vicasol and antihemophilic plasma, isolated fibrinogen, and platelet mass have a special hemostatic effect. The simultaneous administration of too large volumes of donor blood to critically ill patients can lead to a violation of the hemostatic balance with the development of further intravascular blood coagulation.
Nutritional
Donated blood contains not only its cellular components, but also fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Entering the recipient's body, these substances have a nutritious effect. The patient has a surge of vital energy, metabolic processes improve, the work of internal organs is stabilized.
Stimulating
Blood transfusion is a type of substitution therapy that causes stress in the recipient at the cellular level. In the patient's body, physiological changes develop that stimulate the work of the respiratory, cardiovascular, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal, immune systems.
An increase in the phagocytic activity of leukocytes prevents the occurrence of inflammatory processes of infectious etiology. The recipient has a more rapid regeneration of tissues that showed signs of damage.
Main indications for blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is indicated for children, adult men and women who have the following health problems:
- loss of more than 15% of blood as a result of external or internal bleeding;
- state of traumatic shock;
- acute bleeding during a complex surgical operation;
- severe intoxication of the body due to inflammation of an infectious etiology;
- a critical decrease in the protective functions of the immune system;
- anemia;
- hematological diseases associated with blood clotting disorders.

Blood transfusion can be prescribed for patients who have been suffering from a chronic inflammatory process with signs of too slow tissue regeneration for a long period of time.
Indications for the use of blood transfusion drugs
Depending on the clinical diagnosis given to the recipient, whole blood or blood transfusion agents can be used as a donor material.
Whole blood
Whole blood is collected from a healthy donor using non-pyrogenic and sterile anticoagulants. This type of blood transfusion material becomes unusable after storage for more than 1 day.
Whole blood is indicated for transfusion in the following cases:
- an acute decrease in the total volume of circulating blood;
- deficiency of red blood cells;
- lack of other cellular components of the blood.
In medical practice, whole blood is used only in extreme cases, when there are no plasma substitutes, separately isolated erythrocyte, platelet mass or leukocytes. This is associated with a greater risk of developing severe side effects.
Cellular components of blood
There are the following medical indications for the transfusion of individual blood components from donor to recipient:
- decrease in the quantitative number of platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes;
- pathology of the hematopoietic system;
- the period of rehabilitation of the body after prolonged therapy with cytostatics and chemistry preparations;
- a state of chronic or acute blood loss;
- hemolysis of individual blood cells.
Transfusion of cellular components of blood is carried out after a comprehensive examination of the recipient. Patients with signs of thromboembolism and acute renal failure are shown intravenous administration of washed erythrocytes.
Plasma preparations
Transfusion of blood plasma preparations is indicated for patients who suffer from the following pathological conditions of the body:
- liver failure;
- fibrinogen deficiency;
- detachment of the placenta in pregnant women;
- disseminated intravascular blood coagulation;
- hemophilia;
- von Willebrand disease.
Plasma preparations are most often transfused to patients who have suffered severe body injuries, complex surgical operations. Patients in this category need urgent replacement of the missing volume of circulating blood.
Indications for different types of blood transfusion
The indications for blood transfusion are determined by the surgeon, therapist or hematologist who is treating the patient.
Red blood cell transfusion
Red blood cell transfusion is indicated for patients diagnosed with the following disease states of the body:
- severe anemia;
- coronary syndrome;
- blood poisoning;
- ischemic stroke;
- traumatic brain injury.

Red blood cell transfusion is prescribed for patients who, for medical reasons, need to maintain a hemoglobin level at a concentration of more than 90 g per 1 liter of venous blood.
Plasma transfusion
The transfused plasma from a healthy donor should be of the same group according to the ABO classification system, as in a sick recipient.
There are the following direct indications for immediate transfusion of this blood element:
- an acute form of disseminated intravascular coagulation, which is complicated by the manifestation of septic, hemolytic, and hemorrhagic shock;
- severe trauma to the musculoskeletal system with signs of tissue crushing;
- rehabilitation period after a complex surgical operation;
- fulminant hepatitis with an acute course;
- loss of over 30% of the blood circulating in the patient's body;
- cirrhosis of the liver of intoxication or viral etiology;
- overdose with drugs from the pharmacological group of anticoagulants;
- blood poisoning;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- deficiency of plasma anticoagulants;
- extensive intoxication of the body with biological poisons or chemicals.
Transfusion of prepared plasma is carried out by jet or drip method, depending on direct medical indications and the patient's diagnosis. Before starting the transfusion procedure, a biological analysis of the donor material is mandatory.
Platelet transfusion
The indications for blood transfusion are established by the attending physician during the preliminary examination of the patient.
Platelet transfusion is used to stabilize patients with the following health problems:
- acute blood loss as a result of severe injuries;
- the period of recovery of the body after surgery;
- complications of labor (uterine bleeding);
- thrombocytopathy;
- splenomegaly.
Platelet transfusion is not performed in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Specific indications for the transfusion of these blood elements are determined by the doctor based on the patient's diagnosis and the severity of his condition.
Cryoprecipitate transfusion
The main and only indication for the introduction of donor cryoprecipitate is the presence of a diagnosis of hemophilia type A in a sick person, or hypofibrinogenemia. Cryoprecipitate used for transfusion must contain at least 70 units of blood factor VIII. It is necessary that the biological material of the donor is of the same group according to the ABO classification system as that of the recipient.
Cryoprecipitate used for transfusion must contain at least 70 units of blood factor VIII. It is necessary that the biological material of the donor is of the same group according to the ABO classification system as that of the recipient.
Leukocyte transfusion
The components of the leukocyte mass, which are subject to transfusion from donor to recipient, are concentrated granulocytes obtained by apheresis. The standard adult dose of this biological material, which is to be transfused, is 1.5-3 per 10 to the 8th degree of granulocytes per 1 kg of the patient's total body weight.
There are the following indications for blood transfusion of leukocyte mass:
- the patient was diagnosed with a decrease in the concentration of granulocytes in the blood to a level of 0.5 units. by 10 to the 9th degree in relation to 1 liter of venous blood;
- long-term antibiotic therapy with the use of potent drugs;
- blood poisoning in newborns.
A prerequisite for performing a leukocyte mass transfusion is the compatibility of the donor and the patient recipient for the main antigens of the ABO classification system, as well as the rhesus factor. A positive result of this transfusion is the normalization of the patient's body temperature, a decrease in signs of intoxication of the body, and stabilization of the functions of internal organs.
Who can blood transfusions be from?
Blood donors can only be healthy people who have undergone a comprehensive examination of the body, and also meet the criteria specified in the table below.
| Basic criteria for the selection of blood donors | Features of the collection of biological material |
| Age | A blood donor is a citizen aged 18 to 65 years. At the discretion of the medical professional who takes the biological material, the patient's age limit may be limited to 60 years. |
| Health status | At the time of donating blood, the donor must be in good health with no signs of acute or chronic diseases of the body. Blood sampling is strictly prohibited in the presence of the following pathological conditions of internal organs or life support systems:
Blood sampling is temporarily postponed even in patients diagnosed with a cold. For 6 months. It is strictly forbidden to donate to persons who have tattooed or pierced. After dental treatment at a dentist-therapist, you can donate blood no earlier than 1 day later. Do not transfuse blood from women whose hemoglobin level is less than 12 g / dL. For men, this figure is 13 g / dl. |
| Travel | People who have visited non-CIS countries with a tropical climate the day before cannot donate blood. In these regions, mosquito-borne infections are widespread. For example, Zika virus, Dengue fever, malaria. Each donor is obliged to notify medical professionals about recent travel abroad. |
| Lifestyle | Donated blood cannot be transfused from persons in whose lives the following events have previously taken place:
The above restrictions are aimed at preventing infection of the recipient with dangerous infectious diseases. |
| Breastfeeding and pregnancy | Blood donation is contraindicated during lactation. After giving birth, a woman can again become a donor no earlier than 9 months later. |
 All other men and women who do not have health problems, have not visited exotic countries, lead a normal lifestyle, have good test results, and can be blood donors.
All other men and women who do not have health problems, have not visited exotic countries, lead a normal lifestyle, have good test results, and can be blood donors.
Contraindications to blood transfusion
There are the following medical contraindications for transfusion of whole blood or its individual components:
- cardiac diseases;
- pathology of cerebral circulation;
- hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- disturbances in the work of the central nervous system;
- thromboembolism of arterial vessels;
- pulmonary edema, regardless of its nature of origin;
- severe stage of renal failure;
- hypertension of the 3rd degree;
- bronchial asthma;
- a tendency to manifest an allergic reaction.
 Blood transfusion is performed in patients with severe anemia and acute blood loss, but taking into account the potential risk of complications. In this case, drug prevention of the negative consequences of transfusion is performed.
Blood transfusion is performed in patients with severe anemia and acute blood loss, but taking into account the potential risk of complications. In this case, drug prevention of the negative consequences of transfusion is performed.
Complications of blood component transfusion
In hematological practice, there are occasional cases of complications as a result of transfusion of separated blood components.
In such situations, recipients experience the following negative consequences:
- overload of the circulatory system due to too rapid flow of a large amount of blood;
- infection with infectious microorganisms;
- various kinds of allergic reactions in the form of itching of the skin, rash, urticaria;
- post-transfusion injury to lung tissue;
- immune reaction of rejection of donor blood components;
- fever and chills;
- purpura of the post-transfusion type;
- dizziness;
- feeling short of breath.
The appearance of any of the above signs (with the exception of pruritus and urticaria) is the basis for immediate discontinuation of the transfusion. After completing the blood transfusion procedure, the patient receives an intravenous sodium chloride solution.
Blood transfusion is a type of substitution therapy that involves the intravenous infusion of this biological fluid from a donor into the recipient's circulatory system. For this, a drip or jet method of administration is used. Depending on the diagnosis of the patient, his body is saturated with whole blood or its individual components.
Blood transfusion is indicated for patients with acute forms of internal and external bleeding, complications of surgical operations, the consequences of severe body injuries with signs of tissue crushing. Blood donors cannot be drug users, sexually promiscuous people, infected with bacterial, viral, fungal infections, suffering from acute and chronic diseases organism.
Blood transfusion videos
Indications for blood transfusion: